Naftopidil
In this article, we are going to explore in depth Naftopidil and its relevance in today's society. Naftopidil has been a topic of interest for a long time, and its impact spans multiple aspects of modern life. Over the years, extensive research has been conducted on Naftopidil, resulting in a substantial body of knowledge on the topic. In this article, we will examine the different perspectives and approaches that have been taken towards Naftopidil, as well as its evolution over time. Additionally, we will discuss the practical and theoretical implications of Naftopidil in various areas, from politics to science to popular culture. By the end of this article, we hope to have provided a comprehensive overview of Naftopidil and generated a greater understanding of its importance in today's world.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Flivas |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.220.557 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
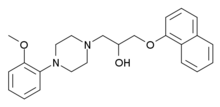
| Formula | C24H28N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 392.499 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Naftopidil (INN, marketed under the brand name Flivas) is a drug used in benign prostatic hypertrophy which acts as a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist or alpha-1 blocker.
Synthesis
The reaction of 1-naphthol (1) with epichlorohydrin (2) in the presence of alkali gives to the epoxide (3). Alkylation of the piperazine derivative (4) yields naftopidil.
See also
References
- ^ Sakai H, Igawa T, Onita T, Furukawa M, Hakariya T, Hayashi M, Matsuya F, Shida Y, Nishimura N, Yogi Y, Tsurusaki T, Takehara K, Nomata K, Shiraishi K, Shono T, Aoki D, Kanetake H (2011). "Efficacy of naftopidil in patients with overactive bladder associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia: prospective randomized controlled study to compare differences in efficacy between morning and evening medication". Hinyokika Kiyo. 57 (1): 7–13. PMID 21304253.
- ^ US patent 3997666, Ernst-Christian Witte, et al., "1--piperazine compounds and therapeutic compositions", issued 1976-12-14, assigned to Boehringer Mannheim GmbH
- ^ Shivani; Pujala, Brahmam; Chakraborti, Asit K. (2007). "Zinc(II) Perchlorate Hexahydrate Catalyzed Opening of Epoxide Ring by Amines: Applications to Synthesis of ( RS )/( R )-Propranolols and ( RS )/( R )/( S )-Naftopidils". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (10): 3713–3722. doi:10.1021/jo062674j. PMID 17411096.
- ^ "Naftopidil". Pharmaceutical Substances. Thieme. Retrieved 2024-07-12.
