Tectospinal tract
| Tectospinal tract | |
|---|---|
 Diagram showing possible connection of long descending fibers from higher centers with the motor cells of the ventral column through association fibers. ("Tectospinal fasciculus" labeled at center right.) | |
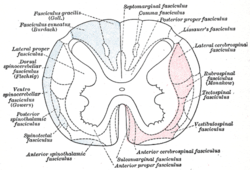 Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. ("Tectospinal fasciculus" labeled at center right, in red.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus tectospinalis |
| MeSH | D065844 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_759 |
| TA98 | A14.1.02.211 A14.1.04.112 |
| TA2 | 6119 |
| FMA | 72620 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In humans, the tectospinal tract (or colliculospinal tract) is a nerve tract that coordinates head and eye movements. This tract is part of the extrapyramidal system and connects the midbrain tectum, and cervical regions of the spinal cord.
It is responsible for motor impulses that arise from one side of the midbrain to muscles on the opposite side of the body (contralateral). The function of the tectospinal tract is to mediate reflex postural movements of the head in response to visual and auditory stimuli.
The portion of the midbrain from where this tract originates is the superior colliculus, which receives afferents from the visual nuclei (primarily the oculomotor nuclei complex), then projects to the contralateral (decussating dorsal to the mesencephalic duct) and ipsilateral portion of the first cervical neuromeres of the spinal cord, the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei in the midbrain and the abducens nucleus in the caudal portion of the pons.
The tract descends to the cervical spinal cord to terminate in Rexed laminae VI, VII, and VIII to coordinate head, neck, and eye movements, primarily in response to visual stimuli.
See also
References
- ^ Pocock, Gillian; Richards, Christopher D. (2006). Human physiology : the basis of medicine (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 152. ISBN 978-0-19-856878-0.